- Introduction
- Overview of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
- Key Features of the ZF 6HP Generation 2
- The Role of Solenoids in the ZF 6HP Transmission
- Understanding the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
- Components of the Solenoid Diagram
- Reading the Solenoid Diagram
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Maintenance Tips
- Final Thoughts
- FAQs about ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
Introduction
The ZF 6HP automatic transmission is a widely recognized and highly regarded piece of automotive engineering. Used in a variety of high-performance and luxury vehicles, this transmission is known for its durability, efficiency, and smooth shifting capabilities. Within this complex system, solenoids play a crucial role in regulating fluid flow and ensuring optimal performance. This article will provide an in-depth look at the ZF 6HP Generation 2 solenoid diagram, explaining its components, functions, and the importance of each part in the overall operation of the transmission.
Overview of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
The ZF 6HP transmission is a six-speed automatic transmission designed by ZF Friedrichshafen AG. It is used in many high-end vehicles, including models from BMW, Audi, Jaguar, and Land Rover. The Generation 2 version of this transmission includes several enhancements over its predecessor, offering improved efficiency, faster shifting times, and greater reliability.
Key Features of the ZF 6HP Generation 2
- Six-speed gear configuration: Offers a wide range of gear ratios for enhanced performance and fuel efficiency.
- Adaptive shift logic: Adjusts shifting patterns based on driving conditions and driver behavior.
- Torque converter with lock-up clutch: Improves fuel efficiency and provides smoother acceleration.
- Enhanced hydraulic control system: Utilizes advanced solenoids to regulate fluid flow and pressure.
The Role of Solenoids in the ZF 6HP Transmission
Electromagnetic valves called solenoids regulate the transmission fluid’s flow inside the transmission system. In the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission, solenoids are responsible for:
- Controlling gear shifts: Solenoids regulate the engagement and disengagement of clutches and brakes, enabling smooth and precise gear changes.
- Managing hydraulic pressure: Solenoids adjust the pressure of the transmission fluid to ensure optimal operation of the transmission components.
- Modulating torque converter lock-up: Solenoids control the lock-up clutch in the torque converter, improving fuel efficiency and reducing heat build-up.
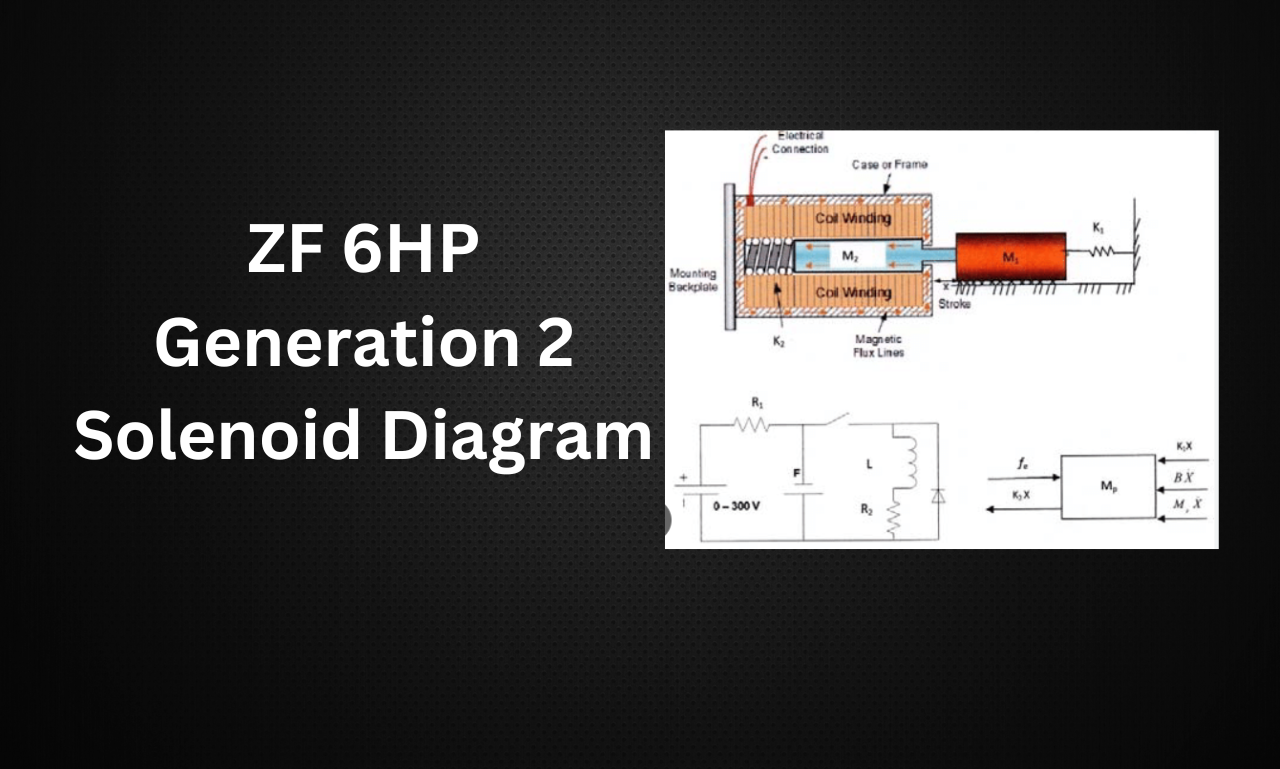
Understanding the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
The solenoid diagram of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission provides a visual representation of the solenoid arrangement and their connections within the transmission. This diagram is essential for understanding the function and location of each solenoid, making it a valuable resource for technicians and enthusiasts alike.
Components of the Solenoid Diagram
- Shift Solenoids: These solenoids control the engagement of the transmission’s gears. They are usually labeled as Solenoid A, Solenoid B, etc., and are responsible for directing fluid to the appropriate clutch packs.
- Pressure Control Solenoids: These solenoids regulate the hydraulic pressure within the transmission. By adjusting the fluid pressure, they ensure that the clutches and brakes engage smoothly and efficiently.
- Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid: This solenoid manages the lock-up clutch within the torque converter, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing slippage.
- Line Pressure Solenoid: This solenoid controls the overall pressure of the transmission fluid, ensuring that the transmission operates within the correct pressure range for optimal performance.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Connections: The diagram will also show the connections between the solenoids and the ECU, which controls the operation of the solenoids based on input from various sensors.
Reading the Solenoid Diagram
When reading the solenoid diagram, it is important to understand the following symbols and notations:
- Solenoid Icons: These typically appear as small boxes or circles labeled with an identifier (e.g., Solenoid A, Solenoid B).
- Fluid Pathways: These are usually represented by lines connecting the solenoids to various components of the transmission.
- Electrical Connections: These are shown as lines or arrows connecting the solenoids to the ECU or other electrical components.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Understanding the solenoid diagram is also crucial for diagnosing and troubleshooting transmission issues. Here are some common problems associated with the ZF 6HP Generation 2 solenoids and how to address them:
Solenoid Failure
Symptoms:
- Harsh or delayed shifting
- Transmission slipping
- Check engine light or transmission warning light
Diagnosis:
- Use a diagnostic scanner to read fault codes related to the solenoids.
- Inspect the solenoid connections and wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion.
Solution:
- Replace the faulty solenoid(s) with OEM parts.
- Verify that every electrical connection is safe and corrosion-free.
Low Hydraulic Pressure
Symptoms:
- Poor acceleration
- Slipping gears
- Overheating transmission
Diagnosis:
- Check the fluid level and quality. Low or dirty fluid can affect hydraulic pressure.
- Inspect the pressure control solenoids and line pressure solenoid for proper operation.
Solution:
- Refill or replace the transmission fluid as needed.
- Replace any malfunctioning pressure control solenoids.
Maintenance Tips
To ensure the longevity and optimal performance of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission, regular maintenance is essential. Here are some tips:
- Regular Fluid Changes: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended intervals for transmission fluid changes. Using the correct type of fluid is crucial for maintaining proper hydraulic pressure and solenoid function.
- Periodic Inspections: Regularly inspect the solenoids, wiring, and connectors for any signs of wear or damage. Early problem identification helps avert later, more significant complications.
- Software Updates: Ensure that the ECU software is up to date. Manufacturers often release updates that can improve transmission performance and address known issues.
Final Thoughts
The ZF 6HP Generation 2 solenoid diagram is a valuable tool for understanding the intricate workings of this advanced transmission system. By familiarizing yourself with the solenoid arrangement and their functions, you can better diagnose issues, perform maintenance, and appreciate the engineering behind this remarkable transmission. Whether you’re a professional technician or an automotive enthusiast, a thorough understanding of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 solenoid diagram will enhance your ability to work with and enjoy this sophisticated piece of automotive technology.
FAQs about ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
- What is the purpose of the solenoid diagram in the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission? The solenoid diagram provides a visual representation of the solenoids’ locations and connections within the transmission. It helps technicians and enthusiasts understand how fluid flow is controlled, aiding in diagnostics, repairs, and maintenance.
- How do solenoids in the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission work? Solenoids in the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission are electromagnetic valves that control hydraulic fluid flow. They receive signals from the ECU to open or close, regulating pressure and directing fluid to engage or disengage gears, clutches, and the torque converter.
- What are common symptoms of a faulty solenoid in the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission? Common symptoms of a faulty solenoid include harsh or delayed shifting, transmission slipping, poor acceleration, and warning lights on the dashboard. Diagnosing these issues often involves reading fault codes and inspecting solenoid connections and wiring.
- Can I replace a solenoid in the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission myself? While replacing a solenoid can be done by a knowledgeable DIYer, it requires specific tools and a good understanding of the solenoid diagram. For those unfamiliar with transmission systems, it’s advisable to seek professional assistance to avoid potential damage.
- How often should the transmission fluid be changed to maintain solenoid function in the ZF 6HP Generation 2? Regular transmission fluid changes are crucial for maintaining solenoid function. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended intervals, typically every 30,000 to 60,000 miles, using the specified fluid type to ensure optimal hydraulic pressure and solenoid performance.